Constitution Resources
Welcome to PLAC's Constitution Resources web page!
Welcome to PLAC's Constitution Resources web page!
This page contains relevant information on Nigeria’s ongoing Constitution review process. The 9th National Assembly (2019 – 2023) is currently reviewing proposed amendments to the 1999 Constitution. Consequently, the Constitution Review Committees of both chambers have invited submissions from the public on areas they want amended. This webpage shares background information on the process and links to pending bills on constitution amendment.
A constitution is an act of the people if it is made by them either directly in a referendum or through a convention or constituent assembly popularly elected for this purpose, subject or not to formal ratification by the people in referendum.
- To improve the existing constitution
- To fill a gap or loophole in the existing constitution
- To respond to political, socio-economic, religious, regional and ethnic concerns by citizens, communities and interest groups.
NASS Constitution Review Committees
S/N | NAMES | MEMBERSHIP | STATE | SENATORIAL DISTRICT | POLITICAL PARTY |
1. | Sen. Ovie Omo-Agege | Chairman | Delta | Delta Central | APC |
2. | Sen. Yahaya Abubakar Abdullahi | Member | Kebbi | Kebbi North | APC |
3. | Sen. Robert Ajayi Boroffice | Member | Ondo | Ondo North | APC |
4. | Sen. Abdullahi Aliyu Sabi | Member | Niger | Niger North | APC |
5. | Sen. Eyinnaya Abaribe | Member | Abia | Abia South | PDP |
6. | Sen. Emmanuel Bwacha | Member | Taraba | Taraba South | PDP |
7. | Sen. Philip Aduda | Member | FCT | FCT | PDP |
8. | Sen. Alhaji Sahabi Ya’u | Member | Zamfara | Zamfara North | PDP |
9. | Sen. Theodore Orji | Member | Abia | Abia Central | PDP |
10. | Sen. Aishatu Ahmed Dahiru | Member | Adamawa | Adamawa Central | APC |
11. | Sen. Stella Oduah | Member | Anambra | Anambra North | PDP |
12. | Sen. Albert Bassey Akpan | Member | Akwa Ibom | Akwa Ibom North East | PDP |
13. | Sen. Halliru Jika | Member | Bauchi | Bauchi Central | PDP |
14. | Sen. Degi Biobarakuma | Member | Bayelsa | Bayelsa East | APC |
15. | Sen. Gabriel Suswam | Member | Benue | Benue North East | PDP |
16. | Sen. Abubakar Kyari | Member | Borno | Borno North | APC |
17. | Sen. James Manager | Member | Delta | Delta South | PDP |
18. | Sen. Gershom Bassey | Member | Cross River | Cross River South | PDP |
19. | Sen. Samuel Egwu | Member | Ebonyi | Ebonyi North | PDP |
20. | Sen. Matthew Urhoghide | Member | Edo | Edo South | PDP |
21. | Sen. Michael Opeyemi Bamidele | Member | Ekiti | Ekiti Central | APC |
22. | Sen. Ike Ekweremadu | Member | Enugu | Enugu West | PDP |
23. | Sen. Danjuma Goje | Member | Gombe | Gombe Central | APC |
24. | Sen. Rochas Okorocha | Member | Imo | Imo West | APC |
25. | Sen. Sabo Nakudu Mohammed | Member | Jigawa | Jigawa South West | APC |
26. | Sen. Uba Sani | Member | Kaduna | Kaduna Central | APC |
27. | Sen. Kabiru Gaya | Member | Kano | Kano South | APC |
28. | Sen. Ahmed Baba-Kaita | Member | Katsina | Katsina North | APC |
29. | Sen. Adamu Aliero | Member | Kebbi | Kebbi Central | APC |
30. | Sen. Smart Adeyemi | Member | Kogi | Kogi West | APC |
31. | Sen. Sadiq Suleiman Umar | Member | Kwara | Kwara North | APC |
32. | Sen. Oluremi Tinubu | Member | Lagos | Lagos Central | APC |
33. | Sen. Abdullahi Adamu | Member | Nasarawa | Nasarawa West | APC |
34. | Sen. Mohammed Musa Sani | Member | Niger | Niger East | APC |
35. | Sen. Ibikunle Amosun | Member | Ogun | Ogun Central | APC |
36. | Sen. Nicholas Tofomowo | Member | Ondo | Ondo South | APC |
37. | Sen. Surajudeen Basiru Ajibola | Member | Osun | Osun Central | APC |
38. | Sen. Teslim Folarin | Member | Oyo | Oyo Central | APC |
39. | Sen. Hezekiah Dimka | Member | Plateau | Plateau Central | APC |
40. | Sen. George Sekibo | Member | Rivers | Rivers East | PDP |
41. | Sen. Aliyu Wammako | Member | Sokoto | Sokoto North | APC |
42. | Sen. Yusuf A. Yusuf | Member | Taraba | Taraba Central | APC |
43. | Sen. Ibrahim Geidam | Member | Yobe | Yobe East | APC |
44. | Sen. Hassan Mohammed Gusau | Member | Zamfara | Zamfara Central | APC |
45. | Sen. Bala Ibn Na’allah | Member | Kebbi | Kebbi South | APC |
46. | Sen. Ibrahim Shekarau | Member | Kano | Kano Central | APC |
47. | Sen. Kasshim Shettima | Member | Borno | Borno Central | APC |
48. | Sen. Lawal Gumau | Member | Bauchi | Bauchi South | APC |
49. | Sen. Tanko Al-Makura | Member | Nasarawa | Nasarawa South | APC |
50. | Sen. Yakubu Oseni | Member | Kogi | Kogi Central | APC |
51. | Sen. Abdulfatai Buhari | Member | Oyo | Oyo North | APC |
52. | Sen. Biodun Olujimi | Member | Ekiti | Ekiti South | APC |
53. | Sen. Uche Ekwunife | Member | Anambra | Anambra Central | PDP |
54. | Sen. Chukwuka Utazi | Member | Enugu | Enugu North | PDP |
55. | Sen. Eyakenyi Akon | Member | Akwa Ibom | Akwa Ibom South | PDP |
56. | Sen. Rose Oko (Deceased) | Member | Cross River | Cross River North | PDP |
S/N | NAMES | MEMBERSHIP | STATE | FEDERAL CONSTITUENCY | POLITICAL PARTY |
1. | Hon. Ahmed Idris Wase | Chairman | Plateau | Wase | PDP |
2.
| Hon. Hassan Doguwa | Deputy Chairman | Kano | Doguwa/ | APC |
3. | Hon. Peter Akpatason | Member | Edo | Akoko Edo | APC |
4. | Hon. Monguno Mohammed Tahir | Member | Borno | Monguno/ | APC |
5. | Hon. Nkeiruka Onyejeocha | Member | Abia | Isukwuato/ | APC |
6. | Hon. Ndudi Elumelu | Member | Delta | Aniocha North/ | PDP |
7. | Hon. Toby Okechukwu | Member | Enugu | Aninri/Agwu/ | PDP |
8. | Hon. Gideon Gwani | Member | Kaduna | Kaura | APC |
9. | Hon. Adesegun Adekoya | Member | Ogun | Ijebu North/ | PDP |
10. | Hon. John Dyegh | Member | Benue | Gboko/Tarka | APC |
11. | Hon. Haruna Mshelia | Member | Borno | Askira Uba/ | APC |
12. | Hon. Aishatu Dukku | Member | Gombe | Dukku/Nafada | APC |
13. | Hon. Usman Danjuma Shiddi | Member | Taraba | Ibi/Wukari | APC |
14. | Hon. Galadima Zakariyau | Member | Yobe | Bade/Jakusko | APC |
15. | Hon. Abubakar Hassan Fulata | Member | Jigawa | Birniwa/Guri/ | APC |
16. | Hon, Tajudeen Abbas | Member | Kaduna | Zaria | APC |
17. | Hon. Ali Muhammad Wudil | Member | Kano | Wudil/Garko | APC |
18. | Hon. Simon Mwadkwon | Member | Plateau | Barkin Ladi/ | PDP |
19. | Hon. Umar Muhammed Jega | Member | Kebbi | Aliero/ | APC |
20. | Hon. Joseph Asuku Bello | Member | Kogi | Adavi/Okehi | APC |
21. | Hon. Uzoma Nkem-Abonta | Member | Abia | Ukwa East/ | PDP |
22. | Hon. Ahmad Yunusa Abubakar | Member | Gombe | Yamaltu/Deba | APC |
23. | Hon. Iduma Enwo Igariwey | Member | Ebonyi | Afikpo North/Afikpo South | PDP |
24. | Hon. Patrick Asadu | Member | Edo | Orhionmwon/ | APC |
25. | Hon. Zainab Gimba | Member | Borno | Bama/Ngala/ | APC |
26. | Hon. Luke Onofiok | Member | Akwa Ibom | Etinan/Nsit Ibom | PDP |
27. | Hon. Salame Balarabe | Member | Sokoto | Illela/ | APC |
28. | Hon. Idris Yerima Abubakar | Member | Yobe | Fika/Fune | APC |
29. | Hon. Beni Lar | Member | Plateau | Langtang North/Lantang | PDP |
30. | Hon. Lawal Umar Muda | Member | Bauchi | Toro | PDP |
31. | Hon. Rimamnde Shawulu Kwewum | Member | Taraba | Takum/Donga/ | PDP |
32. | Hon. Omowumi Ogunlola | Member | Ekiti | Ijero/Ekiti West/ | APC |
33. | Hon. Babajimi Benson | Member | Lagos | Ikorodu | APC |
34. | Hon. Femi Fakeye | Member | Osun | Boluwaduro/ | APC |
35. | Hon. Ibrahim Isiaka | Member | Ogun | Ifo/Ewekoro | APC |
36. | Hon. Adeogun Adejoro | Member | Ondo | Akoko South East/Akoko | APC |
37. | Hon. Sarki Dahiru | Member | Nasarawa | Lafia/Obi | APC |
38. | Hon. Bitrus Kwamoti Laori | Member | Adamawa | Demsa/Lamurde/Numan | PDP |
39. | Hon. Khadija Bukar Abba Ibrahim | Member | Yobe | Damaturu/Gujiba/Gulani/Tarmuwa | APC |
40. | Hon. Ahmed Liman Usman | Member | Katsina | Matazu/Musawa | APC |
41. | Hon. Ahmed Shehu | Member | Zamfara | Bungudu/Maru | PDP |
42. | Hon. Vincent Ofumelu | Member | Anambra | Oyi/Ayamelum | PDP |
43. | Hon. Ikenna Elezieanya | Member | Imo | Owerri Municipal/Owerri North/ | PDP |
44. | Hon. Blessing Onuh | Member | Benue | Otukpo/Ohimini | APGA |
45. | Hon. Daniel Effiong Asuquo | Member | Cross River | Akamkpa/Biase | PDP |
46. | Hon. Ben Igbakpa | Member | Delta | Ethiope East/ | PDP |
47. | Hon. Oberuakpefe Anthony Afe | Member | Delta | Okpe/Sapele/ | PDP |
48. | Hon. Sergius Ogun | Member | Edo | Esan North East/ | PDP |
49. | Hon. Peter Owolabi | Member | Ekiti | Ikole/Oye | APC |
50. | Hon. Ofor Chukwuegbo | Member | Enugu | Enugu North/ | PDP |
51. | Hon. Sokodabo Hassan Usman | Member | FCT | Kuje/Abaji/Gwagwalada/ | PDP |
52. | Hon. Omar Bio Mohammed | Member | Kwara | Baruten/Kaiama | APC |
53. | Hon. Adewunmi Onanuga | Member | Ogun | Ikenne/Shagamu/ | APC |
54. | Hon. Taiwo Oluga | Member | Osun | Ayedaade/Irewole/Isokan | APC |
55. | Hon. Tolulope Akande-Sadipe | Member | Oyo | Oluyole | APC |
56. | Hon. Boma Goodhead | Member | Rivers | Akuku Toru/ | PDP |
57. | Hon. Kingsley Chinda | Member | Rivers | Obio Akpor | PDP |
58. | Hon. Miriam Onuoha | Member | Imo | Isiala Mbano/Okigwe/Onuimo | PDP |
59. | Hon. Lynda Chuba Ikpeazu | Member | Anambra | Onitsha North/Onitsha South | PDP |
60. | Hon. Auwal Jatau Mohammed | Member | Bauchi | Zaki | PDP |
61. | Hon. Sada Soli | Member | Katsina | Jibia/Kaita | APC |
62. | Hon. Shehu Koko | Member | Kebbi | Koko Besse/Maiyama | APC |
63. | Hon. Komsol Longgap | Member | Plateau | Mikang/Qua-anpan/Shedam | APC |
64. | Hon. Alhassan Kabiru RumRum | Member | Kano | Rano/Bunkure/Kibiya | APC |
65. | Hon. Aminu Ibrahim Malle | Member | Taraba | Jalingo/Yorro/ | PDP |
Issues for the 9th NASS Public Hearings
Senate
- Gender Equity/Increased participation of Women and Vulnerable groups in governance
- The Federal Structure in governance and Power Devolution
- Local Government Administration/Local Government autonomy
- Public Revenue, Fiscal Federalism and Revenue Allocation
- Constitutional Provision for the Establishment of State Police
- Judicial Reform - Adjudication of election and pre-election matters and other justice delivery concerns.
- Electoral Reforms that will make INEC deliver transparent, credible, free and fair elections, Political parties, Independent candidature and election management
- Socio-economic rights as contained in Chapter II of the Constitution.
- Residency and indigeneship
- Immunity – Removal of immunity in prima facie criminal cases
- Time-line for Assent of Bills and Passage of Appropriation Bill
- States and Local Government Creation
- Strengthening the independence of institutions like the office of the Accountant General of the Federation, Auditor General of the Federation and Office of the Attorney General of the Federation.
- F.C.T. Administration
- The Legislature and Legislative Bureaucracy
- Constitutional Roles for Traditional Rulers
- Any other issue that promote the unity and good governance of the Nigerian nation.
House of Representatives
- Electoral Matters
- Local Governments
- Judiciary
- Fundamental Human Rights
- Gender equity and increased participation of women and vulnerable groups in governance
- Immunity
- Indigeneship and Residency
- Devolution of Power
- Strengthening the Independence of Institutions
- Traditional Institutions
- States and Local Governments Creation
- Legislature and Legislative Bureaucracy
The Constitution Amendment Process
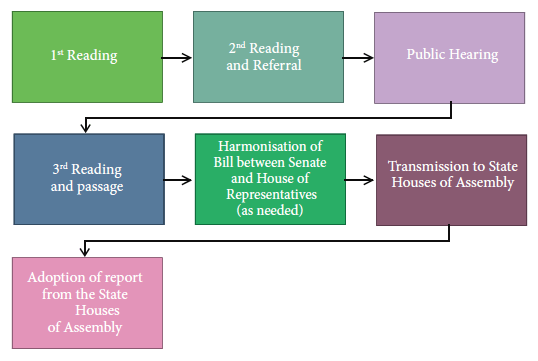
The Constitution stipulates that any amendment to the Constitution has to come by way of an Act. However, it is processed in a manner distinct from ordinary bills as it goes through a more stringent procedure. While Section 9 of the 1999 Constitution details the steps in amending its provisions, it contains no provision on the methodology or timelines to be adopted in developing or adopting amendment proposals or clauses. It also makes no provision for a referendum.
A legislator, group of legislators, the executive or judiciary may propose an amendment to the Constitution. Individuals or groups seeking an amendment may also do so, but through their legislators. Submission of memoranda and participation in public hearings are also platforms through which citizens can propose amendments to the Constitution.
The Amendment Process
- A Constitution amendment proposal is usually addressed to the Presiding Officer of the Senate or House, who then refers the bill to their respective Rules and Business Committees for scheduling on the Order Paper for introduction.
- Proposed amendments are usually considered at separate sittings of each House. The consideration of a Constitution Amendment Bill in each House is as follows:
- First Reading: Here, the long title of the bill is read by the Clerk of the House.
- Second Reading: After the bill is read a second time and its general principles debated, the proposed amendments are forwarded to the Committee on the Review of the Constitution.
- The Committee then reviews the bill and organizes public hearings for further consultations.
- The amendment proposals are then compiled into one or separate bills and presented to the Chamber at its Plenary. Every legislator has to vote either in support or against each specific clause in the Bill. A two-thirds majority of all the members of each house or chamber is needed for each clause to pass.
Note that: where it borders on the creation of new states, boundary adjustments, new local government areas, fundamental human rights and the mode for altering the Constitution, a four-fifths majority is needed.
- If the bill meets the required threshold, it progresses to the Third Reading stage.
- If two-thirds of each chamber pass the bill without amendments or differences, it is then transmitted to the State Houses of Assembly for concurrence. However, if an amendment occurs at either of the chambers or there are differences in the Senate and House of Representatives versions respectively, a Conference Committee will be set up to harmonise differences on the bill before sending it to the States for concurrence. Note that if both Houses are not able to harmonise positions, the Bill will be returned to the respective chambers for fresh voting.
- At the State Assembly level, a simple majority vote of approval of each clause by two-thirds of the States is required for each amendment to come into effect. This is about 24 of Nigeria’s 36 States. Note that in practice, State Assemblies have been known to “step down” or “defer” a bill they are unable to decide on instead of voting “No.” This still does not translate to a “Yes” vote.
- Following concurrence by the States, they send reports on their voting on the bill(s) back to the National Assembly for adoption. Thereafter, the Clerk of the National Assembly sends a clean copy of the Bill(s) to the President for assent.
Note that the Constitution does not expressly prescribe the requirement of the President’s Assent for constitution amendment bills, however, the Federal High Court in a 2010 decision ruled that the President's signature is required since constitution alterations come by way of an Act. It has also been argued that it is a way of ensuring checks and balances.
For more details on Process of Amendment of the Constitution, see: PLAC Step-by- Step Guide to the Process of Amending the Nigerian Constitution
Quick Facts on Amendments to Nigeria's Constitution
- The Constitution can be defined as the organic law of the land from which all other laws derive their validity. It is also referred to as the “Grundnorm.” Nigeria’s Supreme court describes it as “a system or body of fundamental principles according to which a nation, a state, or body or organisation is constituted and governed.”
- Nigeria has experienced many constitution changes since the colonial period. These colonial constitutions were not democratic, as they did not meet the minimum requirements of a democratic constitution. Many say that Nigeria has never had a truly democratic constitution through the years of 1960, 1963, 1979 and even with the 1999 Constitution of the 4th Republic. The 1999 Constitution, which was adopted on May 29, 1999, is in many ways, a revival of the 1979 Constitution.
- Nigeria operates a rigid Constitution, which means that the process for its amendment is cumbersome and time consuming. In spite of this, Nigeria has had four successful amendments to the Constitution namely the First, Second, Third and Fourth Constitution Alteration Acts. The Constitution as it is presently drafted, does not provide for how the people can create an entirely new Constitution. Therefore, only a piecemeal or incremental approach to amendment is currently possible.
- In 2010, the 6th National Assembly was able to successfully amend the 1999 Constitution for the first time. Several provisions of the Constitution dealing with electoral matters were amended. Following this, the Electoral Act was also amended in line with the Constitution amendments. Another notable constitution amendment in the 6th National Assembly was the inclusion of the the National Industrial Court of Nigeria as a court of superior record.
- The 2010 constitution amendment was a major milestone in the history of constitution making in Nigeria because it was the first time that a democratically elected legislature had succeeded in amending the Constitution. Previous amendments to the Nigerian Constitution had been made by either the colonial or military regimes.
- Despite the forgoing significant legislative success recorded in the 6th National Assembly, more agitations were canvassed in the 7th National Assembly which resulted in the 4th Constitution Alteration Bills to address many unresolved contentious national issues which were either not accommodated by the previous Alteration Acts or which emerged in response to political, socio-economic, religious, regional and ethnic concerns by many Nigerians.
- The House of Representatives adopted a new approach of engaging public participation in the Alteration making process via hearings called the “Peoples Public Session” in the 360 federal constituencies, while the Senate maintained its conventional approach through public hearings at National and Zonal Levels.
- The 7th National Assembly was successful in obtaining consensus on many key issues. Till date, their amendments remain the most ambitious and comprehensive revision to the 1999 Constitution, addressing a wide range of issues canvassed by citizens. About 66 sections and six schedules were amended. Unfortunately, the bill was not assented by Former President Goodluck Jonathan primarily due to a proposed amendment to section 9, which sought to dispense with the President’s signature in constitution amendment. This led to a deadlock which was not resolved by the Supreme Court, to whom the matter was presented before the end of the administration.
- Constitution Alteration efforts since the 6th National Assembly have been mostly last minute. Most often, the alteration exercises were rounded up at the very tail end of the tenure of the Assembly that embarked upon it.
Bills Referred to the 9th NASS Constitution Review Committees Based on Information from Its Votes and Proceedings
Since the inauguration of the 9th National Assembly, several constitution amendment bills have been proposed by lawmakers and referred to the Ad-hoc Committee for further legislative action.
The 1999 Constitution Alteration Bills currently before the committee and expected to be considered in the review process include the following:
- SB 323: A Bill to Alter sections 31 and 318 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for indigeneship by application;
SB 324: A Bill to Alter sections 65 and 106 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the identification of women as indigenes of a State by marriage when running for office;
SB 336: A Bill to Alter sections 76,116,132,178 and 285 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the expansion of the time for elections to the National Assembly, State Houses of Assembly, the office of President, and office of Governor, and amendment of the time for the determination of pre-election matters so as to provide sufficient time for the conduct of party primaries and final determination of pre-election matters by the courts prior to the election day;
SB 325: A Bill to Alter sections 147, 171 and 192 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to specify the minimum number of Youths and Women appointed as Ministers, Ambassadors and State Commissioners;
SB 326: A Bill to Alter section 213 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to specify the time frame for the conduct of population census;
SB 318: A Bill to Alter section 251 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to preclude the Federal High Court from entertaining pre-election disputes emanating from congresses, conferences, conventions or other meetings convened by political parties for the purpose of electing members of its executive committees or other governing bodies;
SB 319: A Bill to Alter section 257 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to preclude the High Court of the Federal Capital Territory from entertaining pre-election disputes emanating from congresses, conferences, conventions or other meetings convened by political parties for the purpose of electing members of its executive committees or other governing bodies;
SB 320: A Bill to Alter section 272 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to preclude the High Court of a State from entertaining pre-election disputes emanating from congresses, conferences, conventions or other meetings convened by political parties for the purpose of electing members of its executive committees or other governing bodies;
SB 321: A Bill to Alter section 285 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the establishment of separate Tribunals to hear and determine Pre-election matters and Election petitions respectively, in the Presidential, National and State Houses of Assembly, and Governorship elections;
SB 204: A Bill to Alter sections 64,105 and 311 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to designate a definite day for convening the first session and inauguration of elected Members of the National Assembly and State House of Assembly and to provide saving provisions regarding the Standing Orders of the legislative houses dissolved by the President and Governor;
SB 48: A Bill to Alter sections 82 and 122 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to reduce the period within which the President or the Governor of a State may authorize withdrawal of monies from the Consolidated Revenue Fund in the absence of an Appropriation Act from 6 months to 3 months; and for other purpose;
SB 75: A Bill to Alter sections 65,131, 106 and 177 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the Minimum Qualification for election into the National and States Assembly, Office of the President and Governors, and Other related matters;
SB 259: A Bill to Alter sections 81 and 121 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to specify the period within which the President or Governor of a State presents the Appropriation Bill before the National Assembly or House of Assembly, and other related matters;
SB 248: A Bill to Alter section 214 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the establishment of State Police and to ensure effective community policing in Nigeria and for matters connected thereto;
SB 73: A Bill to Alter the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to amend sections 138 and 139 of the Electoral Act, 2020 to reduce the unlawful exclusion of a political party Logo on a Ballot Paper to a Pre-election matters;
SB 306: A Bill to Alter sections 34, 35, 39, 214, 215, 216 and Third Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to replace the name “Nigeria Police Force” with “Nigerian Police” to reflect their core mandate of providing Civil Services;
SB 274: A Bill to Alter sections 3 and 4 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to give recognition to the Six Geo-political Zones and to further introduce clear demarcation by creating the Federal and State Legislative list as a substitute to the existing legislative lists;
SB 316: A Bill to Alter sections 34(2), 35(3)(b), 42(3), 84(4), 89(2), 129(2), 162(2), 197, 214, 215, 216, Second Schedule, Part I of the Third Schedule, and Part II of the Third Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the establishment of State Police;
SB 109: A Bill to Alter section 162 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to give Local Government Council direct control of their Finances;
SB 218: A Bill to Alter section 162 (2) of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for an upward review of the Derivation Formula for the inclusion of Solid Minerals and Hydro Power in the Derivation Principle;
SB 240: A Bill to Alter sections 16 and 33 of the 1999 Constitution to make provisions for Right to Food and Food Security in Nigeria;
SB 335: A Bill to Alter sections 7(4), 7(5), 65 (2)(b), 65(2)(c), 106(d), 106 ( e), 131(e), 131(d), 171 (c), 171(d), and 171(e) of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make provision for independent Candidate in an election to the offices of President, Governor, Senator, House of Representatives, House of Assembly, Chairman and Councilors of LGA/Area Councils of the FCT;
SB 357: A Bill to Alter the First Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make provision for the change of the name of the Area referred to as “Egbado” in Ogun State to “Yewa”
SB 361: A Bill to Alter sections 48, 49, 71, 147, and 300 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to allow for more representation in the National Assembly for the Federal Capital Territory, Abuja;
SB 322: A Bill to Alter sections 308 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to qualify criminal liability for certain public officers; and to provide for qualification of the immunity clause to exclude immunity for Public Officers referred to in section 308 from criminal liability where the offence involves misappropriation of funds belonging to the Federal, State or Local Government and also the use of thugs to foment violence;
SB 253: A Bill to Alter sections 4, 51, 67, 68, 93 and 109 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide immunity for Members of the legislature in respect of words spoken or written at Plenary Sessions or Committee proceedings and institutionalise legislative bureaucracy in the Constitution;
SB 184: A Bill to Alter section 162 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make Financial Provisions for the Financial Autonomy of Local Government Councils;
SB 253: A Bill to Alter section 253 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to reflect the establishment and core functions of the Nigeria Security and Civil Defence Corps;
SB 327: A Bill to Alter sections 1 and 2 of the Sixth Schedule to provide for a Committee comprised of the Chief Justice of Nigeria, President of the Court of Appeal and Chief Judge of the Federal High Court to appoint Tribunal Judges for Presidential, Governorship and National Assembly Election Petition;
SB 74: A Bill to Alter section 54 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for quorum at the inaugural sitting of the National and State Assembly;
SB 514: A Bill to Alter section 14 and Part I of the Third Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the Federal Character;
SB 261: A Bill to Alter section 9 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the procedure for passing a Constitution Alteration Bill where the President withholds assent;
SB 276: A Bill to Alter sections 34(2), 162(2), 162(4) of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to constitutionally end degrading, treatment of suspects arrested and in detention; to promote equity in distribution of Revenue derivable from sources within a locality by ensuring more funds to areas of derivation;
SB 275: A Bill to Alter section 285 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to address the issue of intervening event occurring within the stipulated period for hearing and determination of an election petition or appeal before a tribunal or court of appeal;
SB 388: A Bill to Alter Part I of the First Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make provision for change of name of the area referred to as ‘afikpo’ in ebonyi state to ‘edda’
SB 399: A Bill to Alter sections 65, 106, 131, 132(3) of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make provisions for independent candidacy in general elections in Nigeria
It would be recalled the President of the Senate, Sen. Ahmad Lawan (APC: Yobe) had announced the Membership of the Ad-hoc Committee on Review of the 1999 Constitution at the Senate’s plenary session of Thursday, 6 February 2020.
- HB 754: A Bill to Alter sections 65, 106 and 177 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to allow for a private candidate to stand for an elective position in Nigeria not being sponsored by any of the registered political party.
- HB 899: A Bill to Alter sections 77 and 117 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for Diaspora Voting.
- HB 996: A Bill to Alter section 285 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make further provisions relating to time within which to file and determine election petitions and appeals.
- HB 1059: A Bill to Alter sections 142 and 187 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to preserve the elections of candidates to the Office of the President or Governor whose Deputies have been found to have deficiencies in their qualifications.
- HB 338: A Bill to Alter section 7 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make comprehensive provisions for the Offices of the Local Government Council Chairman, Vice Chairman, and Councilors and guarantee their tenures.
- HB 505: A Bill to Alter section 7 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for the financial and administrative autonomy of Local Government Councils and uniformity of tenure across the country.
- HB 153: A Bill to Alter Part 1 of the Third Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to establish the independence of the National Judicial Council (NJC) by allowing Members of NJC appoint their own Secretary rather than being recommended for appointment from outside the NJC by a lower body of the Federal Judicial Service Commission.
- HB 840: A Bill to Alter sections 291 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to allow for constituency in the retirement age and allowances of Judicial Officers of Superior Courts of record.
- HB 1056: A Bill to Alter sections 287 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to set time within which civil and criminal causes and matters are heard and determined at trial and appellate courts in order to eliminate unnecessary delay in administration of justice.
- HB 1062: A Bill to Alter sections 121, 124, Part II of the Third Schedule, 84, 162, 197, 201, 271, 276, 281, 289, 292 and Part I of the Third Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide a legal framework for financial and administrative independence for the State Judiciary and establish the State Judicial Councils.
- HB 1063: A Bill to Alter section 254 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to delete the entire provisions on the ground that the Evidence Act, the Criminal Procedure Act and Criminal Procedure Code are repealed and replaced by the Administration of Criminal Justice Act; and that the Evidence Act and Administration of Criminal Justice Act contain specific provisions which make each applicable to Federal Offences regardless of Court.
- HB 218: A Bill to Alter sections 150, 174, 195, 211 and 315 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to introduce the Office of the Attorney General of the Federation distinct and separate from the Office of the Minister.
- HB 596: A Bill to Alter sections 18, 45, and 318 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make free, compulsory and basic education a fundamental right of all citizens under Chapter IV.
- HB 325: A Bill to Alter section 308 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to extend immunity to the Presiding Officers of the Legislative Arm of Government.
- HB 767: A Bill to Alter section 308 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to restrict legal proceedings against the Chief Justice of Nigeria, the Justices of the Supreme Court of Nigeria, the Chief Judge of the Federal High Courts and the Chief Justices of the State High Courts and FCT.
- HB 612: A Bill to Alter sections 26 and 28 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for citizenship by Marriage.
- HB 106: A Bill to Alter sections 81 and 82 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to ensure that the Appropriation Act commences on the first day of January of every year.
- HB 328: A Bill to Alter Part I of the Third Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to include presiding officers of the National assembly in the Membership of the National Security Council.
- HB 359: A Bill to Alter sections 147 and 192 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to set a timeframe for submitting the names of Ministerial Nominees or Commissioners with portfolios attached and evidence of declaration of assets and liabilities prior to confirmation.
- HB 440: A Bill to Alter sections 4 and 6 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to strengthen the principle of separation of powers and guarantee the independence of different Arms of Government.
- HB 511: A Bill to Alter section 89 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to prescribe as an offence the Contempt of a Legislative House.
- HB 839: A Bill to Alter section 121 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to reflect the authority of persons mandated to make and receive payment for funding of Houses of Assembly and Judiciaries of States from the Consolidated Revenue Fund of the Federation.
- HB 1216: A Bill to Alter sections 67 and 108 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to grant the two chambers of the National Assembly and the State Houses of Assembly powers to summon the President of the Federal Republic of Nigeria and Governors of States to answer questions on issues of national security or any matter whatsoever, over which the National Assembly and State Houses of Assembly have power to make laws.
- HB 804: A Bill to Alter sections 153, 197 and the Third Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide for Traditional Rulers Council to advise the President and Governors on culture and tradition and help in maintaining peace and order in their traditional domain.
- HB 1111: A Bill to Alter section 215 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to make the appointment of Commissioner of Police of States subject to the recommendation of the Inspector General of Police and make the recruitment of Constables and Cadets the responsibility of the IGP.
- HB 755: A Bill to Alter Part I of the Second Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to devolve to States some items in the Exclusive Legislative List.
- HB 950: A Bill to Alter Part II of the Second Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to amongst others, transfer the subject matter of Minimum Wage from the Exclusive Legislative List to the Concurrent Legislative List.
- HB 1070: A Bill to Alter Part I of the Second Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to provide that the Federal and State Governments shall have Concurrent Legislative Authority with respect to Railway.
- HB 1164 : A Bill to Alter Part 1 of the Second Schedule of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to remove prisons from the Exclusive Legislative List and to provide for the establishment of Correctional Centres in the Concurrent List.
- HB 1235: A Bill to Alter section 254 of the 1999 Constitution (as amended) to transfer Labour, Industrial Relations, Industrial Dispute and Minimum Wage from the Executive Legislative List to the Concurrent Legislative List.
Outcome
Constitutional Amendment Bills that were Assented/Signed into law by the President
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 1) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 2) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 3) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 4) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 5) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 6) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 8) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 9) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 10) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 12) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 15) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 16) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 17) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 23) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 32) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration, No. 34) Act, 2023
- Constitution of the Federal Republic of Nigeria, 1999 (Fifth Alteration) (No. 37) Act, 2023
Useful Resources
Useful Resources
Previous Constitution Amendment Efforts
The 7th National Assembly was inaugurated in 2011 while their respective Ad-hoc Constitution Review Committees were set up in early 2012. The Senate committee was headed by then Deputy Senate President, Ike Ekweremadu, while that of the House of Representatives was headed by then Deputy Speaker, Emeka Ihedioha.
The Committees issued calls for memoranda from the public via advertisements in both the print and electronic media. The call for memoranda by both chambers highlighted the following priority issues:
Fiscal Federalism; Financial Autonomy and Independence of State Houses of Assembly and Local Government Councils; Mode of Alteration of the Constitution; Citizenship and Indigene-ship question; Justiciability of Chapter II of the Constitution; Independent Candidacy in Elections; Diaspora Voting; Separation of the Office of the Attorney-General of the Federation from that of the Minister of Justice; Removal of Immunity for the President, Vice President, Governors and Deputy Governors on criminal matters; Devolution of Powers from the Federal level to the States; Reduction of the items on the Exclusive Legislative List, etc.; Prohibition of interlocutory appeals in election matters; Introduction of Single Tenure of Office; Abolition of the existing bicameral legislature; Rotation of power among the geo-political zones; Abolition of States Independent Electoral Commissions; Creation of new States; Establishment of State Police; Mayoral Status for the Federal Capital Territory, Abuja; Constitutional role for traditional rulers; Recognition of the Six Geo-political Zones in the Constitution; Deleting the following Acts of the National Assembly from the Constitution: The Land Use Act, NYSC Act, Public Complaints Commission Act and the National Security Agencies Act (Section 315); Amendment of provisions related to amendment of the Constitution, State Creation and Boundary Adjustment to remove ambiguities; Rotation of Executive Offices; Gender and Special Groups.
Civil society organizations, professional associations, communities, several interest groups and members of the general public responded to this call by submitting memoranda to the National Assembly. They also mobilised participation in nationwide public hearings, which was called the “People’s Public Sessions” by the House of Representatives and held all over the 360 Federal Constituencies. The Senate on its part, held zonal and national hearings.
Outcome
The National Assembly developed bills based on submissions and responses from the public hearings. About 66 sections were amended and put into one single bill. Unfortunately, the bill was vetoed by the former President, Good luck Jonathan over contentious clauses in the bill and this could not be resolved before the end of the 7th Assembly.
Link to Summary of Constitutional Provisions Amended by the 7th National Assembly, Adopted by the State Houses of Assembly and Transmitted for Assent
Letter of President Goodluck Jonathan withholding Assent to the Constitution Alteration Bills
Following the failure of the constitution amendment bill of the 7th Assembly, the 8th Assembly adopted a different strategy of putting amendment proposals in separate bills based on subject matter. The aim was to avoid lumping contentious provisions with amendments on which consensus had been built or which stood a better chance of passage. With the 7th Assembly, the disagreement between the executive and legislature over dispensing with the President’s signature for Constitution alterations in section 9 led to the failure of every other amendment as the provisions were all contained in one single alteration bill.
Following the change in strategy, the 8th Assembly was able to successfully amend a number of provisions of the Constitution. Out of about 12 separate bills transmitted to the President, 5 were assented.
Outcome
Constitutional Amendment Bills that were Assented/Signed into law by the President
- Financial Autonomy for State Legislatures and Judiciary - Section 121
- Political Parties and Electoral Matters - Sections 134, 179 and 255A
- Restriction on Tenure of the President and Governor - Sections 137 and 182
- Determination of Pre-Election Matters - Section 285
- Reduction of Age for Certain Elective Offices - Sections 65, 106 and 131
Constitution Amendment Bills Vetoed by the President
- The Legislature - Sections 4,51,67,68, 93 and 109
- Consequential Amendment on Civil Defence - Section 213
- Procedure for Overriding Presidential Veto in Constitution Alteration - Section 9
- The Nigeria Police Force - Sections 34, 35, 39, 214, 215, 216 and Third Schedule
- Authorisation of Expenditure 1 - Sections 82 and 122
- Authorisation of Expenditure 2 - Sections 81 and 121
- Submissions from the Judiciary
Letter of President Muhammadu Buhari withholding Assent to the Constitution Alteration Bills
Constitution Amendment Bills not Adopted by State Assemblies
- Distributable Pool Account - Section 162
- Local Government - Sections 7, 318, and Part 1 of Fifth Schedule
- Independent Candidature - Sections 7, 65, 106, 131, 177 and 228
- Presidential Assent - Section 58
- Financial Independence for the Office of the Auditor-General of the Federation and the State - Sections 81 and 121
Constitution Amendments Bills passed with differences by the two chambers
- Composition of Council of States - Third Schedule of the Constitution
- Separation of Office of the Accountant General of the Federal Government from the Office of the Accountant General of the Federation - Section 84
- Investment and Securities Tribunal - Sections 6, 84, 240, 243, 254, 292, 294, 295, 318, Third and Seventh Schedules
- Timeframe for submission of the names of ministerial/commissioner nominees respectively - Sections 147 and 192
Constitution Amendment Bills proposed by the Constitution Review Committees but not passed by the National Assembly
- Devolution of Powers - Second Schedule (rejected by both Houses)
- State Creation and Boundary Adjustment - Section 8 (rejected by both Houses)
- Appointment of Minister from FCT - Section 147 (passed by only Senate)
- Change of Name of Some Local Government Councils - First Schedule (passed by only Senate)
- Separation of the office of the Attorney-General of the Federation and State from the Minister/Commissioner for Justice - Sections 150, 174, 195 211, 318, Third Schedule (passed by only Senate)
- Deletion of NYSC Decree, Public Complaints Commission, National Securities Agencies Act from the Constitution - Section 315 (passed by only Senate)
- Deletion of Land Use Act from the Constitution - Section 315 (rejected by both Houses)
- Deletion of State Independent Electoral Commission (SIEC) from the Constitution - Section 197, Third Schedule Part II (passed by only Senate)
- Citizenship and Indigeneship - Section 26 - to give constitutional backing to the rights of married Nigerian women to claim either the indigene status of their spouses’ state or their own state of origin (rejected by both Houses).
Key Dates
Wednesday, 26th May - Thursday, 27th May, 2021: Zonal Public Hearings on Constitution Alteration Bills by the Senate Ad-hoc Committee on Constitution Review.
Thursday, 3rd June - Friday, 4th June, 2021: National Public Hearing on Constitution Alteration Bills by the Senate Ad-hoc Committee on Constitution Review.
Tuesday, 1st June - Wednesday, 2nd June 2021: Zonal Public Hearings on Constitution Alteration Bills by the House of Representatives Ad-hoc Committee on Constitution Review.
Glossary of Legislative and Constitutional Terms
Act
A bill passed by the legislature.
Action
Any step of legislative procedure relating to a proposed law.
Ad Hoc Committees
Committees appointed for special purposes which are dissolved upon completion of assignment.
Adjourn
Discontinuation of legislative proceedings, often to prevent further consideration of an issue.
Adjournment
Termination of legislative activities at the conclusion of each legislative day with indication of the next day’s meeting time. Also refers to termination of legislative activities at the ending of the (first) regular session of a Legislature.
Adoption
Indicates approval or acceptance and can refer to amendments or entire legislative measures.
Amendment
Any modification, deletion, or addition, which alters form or substance of legislation. A change proposed to a motion, a bill, a written question or a committee report with the intention of improving it or providing an alternative. “Amendment” does not include replacing the entire constitution.
Appropriation
A legislative authorisation to make expenditures and incur obligations.
Bicameral
A two-house legislature.
Bill
A proposed law that the National Assembly or a State Assembly is asked to consider.
Budget
Estimates of proposed expenditures and expected revenues for a fiscal year.
By-law
Rule made by a local body or council under authority of a statue.
By-election
Held to fill vacancies in the legislature which arise before the end of the legislative term.
Caucus
A group of party members often formed within the legislature to develop strategies for promoting party ideology.
Chair
The presiding officer at a meeting of the National Assembly or a Committee.
Clerk
An officer of the House or Senate who is responsible for its operation and other legislative staff.
Committee
A body of legislators of a chamber - Senate or House of Representatives - appointed for a special or general purpose or to perform specific tasks. The chamber may delegate any functions exercisable by it to its committees but they do not have final decision making authority and can only make recommendations to the chamber on any matter referred to it.
Concurrence
Agreement. Means that one House “accepts” the actions of the other House.
Concurrent
At the same time as.
Concurrent power/legislative list
Powers that are shared by federal and state governments under the constitution. The concurrent legislative list in the 2nd schedule to the 1999 Constitution defines areas in which both the National and State Assemblies can legislate. Where laws in an area of concurrency conflict, the federal law supersedes.
Conference Committee
A committee of members of the House and Senate that confers on differences in a bill, which have passed both Houses.
Confirmation
Senate action with respect to executive appointments requiring advice and consent.
Consolidated Revenue Fund
Federal Government purse/account into which its income and revenues are paid and from which public expenditure is met; exclusively owned and managed by the Federal Government. The National Budget is funded from the Consolidated Revenue Fund of the Federation while State budgets are funded from the Consolidated Revenue Fund of the State.
Consolidation (of bills)
Different bills on the same subject merged together.
Consensus
A general agreement about something or on an issue. Does not have to be unanimous.
Consideration
To discuss or review a bill either by legislators or a committee with the view to reaching a decision.
Constituency
A geographically defined area or unit in which voters elect one or more representatives to the legislature. Also called electoral district.
Constituent assembly
An entity or body created and elected by the people to prepare a constitution. This may or may not be the legislature but should have constituent power i.e. the legal power and the people’s authority to create a constitution. The form of such assemblies varies widely across jurisdictions and members may be elected by popular vote or chosen through other means.
Constituent unit
A constitutionally recognised geographical unit in a federation, such as a state. In federal systems, the constitution divides sovereign powers between a federal authority and the constituent units i.e. the states
Constitution
The supreme or fundamental law of a country; a foundation upon which other laws or norms derive their validity. It outlines the structure and operation of institutions of governance, rules of procedure of that government, rights and responsibilities of citizens, use of public funds, etc.
Constitutional review
A process of considering whether an existing constitution ought to be amended which may or may not end in a new constitution. In the Nigerian context, it refers to the actual process of altering the provisions of the constitution.
Constitutional reform
Amendment or replacement of the constitution or wider changes in society and governance.
Constitutionalism
A practice or philosophy of adherence to constitutional principles involving limits on the power of the government put by those constitutional principles and words of the constitution.
Constitutionality
Acting in accordance with the provisions or principles of a constitution
Debate
A discussion of a subject under consideration by the legislature. It could be on a bill or motion before the chamber.
Decentralisation
Transfer of power from the central government to the states and local governments to enable exercise of administrative, legislative and/or fiscal authority.
Deliberation
Fair consideration of all positions by the legislature, guided by facts, reason, the values of democracy and the general welfare before decision making.
Democracy
A system of government by and for the people. Literally means ‘rule by the people’.
Devolution
Governmental power is passed over from the central or national government to lower levels of government. Devolution involves transfer of political powers whereas decentralization usually refers to the transfer of administrative or fiscal powers.
Directive principles
Principles and policies focusing on citizens’ welfare formulated as guidelines for the state such as those contained in Chapter 2 of the 1999 Constitution. Usually not justiciable i.e. unenforceable in court.
Drafting
Expert task of putting constitutional ideas into precise legal language that those who will employ the constitution, including the courts, are able to interpret. Usually done by legal drafters.
Election
The process of selecting a person of choice through voting.
Election petition
Questions on the validity of an election which is presented to a court or tribunal.
Electoral system
Rules and method of converting votes into seats in an elected body.
Enact
To make or pass a law.
Enacting Clause
The phrase preceding the provisions of a bill which identifies the legislative body responsible for its creation. Usually worded “Be it enacted by the National Assembly ...”
Entrenched
Guaranteed in the constitution and difficult to change
Exclusive power/legislative List
Powers reserved exclusively for the central or federal government. Items in the exclusive legislative list in the 2nd schedule to the Constitution are assigned to the federal government; only the National Assembly can legislate on those items.
Federation Account
Also called “Distributable Pool Account” from which allocations are made to the Federal, State and Local governments. It is made up of revenues collected by the government (excluding personal income tax/PAYE of armed forces and police personnel, foreign services personnel and FCT Abuja residents). Held in trust by the Federal Government on behalf of the three tiers of government for distribution in accordance with a formula prescribed by law.
First-Past-the-Post system
Electoral system where a candidate who receives more votes than any other candidate gets elected irrespective of the vote share.
Floor
Reference to the interior of a legislative chamber where plenary discussions take place.
Franchise
The right to vote.
Hansard
The official printed record of debates in the National Assembly.
Hearing
A formal session of a Legislative Committee at which business is conducted or testimony is received or meeting at which witnesses from the general public are invited to participate.
Judicial review
Powers of the courts to decide upon the constitutionality of a legislative or an executive act and invalidate that act if it is determined to be contrary to constitutional provisions or principles.
Journal
An official record maintained by each House reporting essential items of daily business, indicating specific action and recording votes.
Justiciable
Something which can be taken to court for a legal ruling.
Legality
Lawful; in accordance with the law.
Legitimacy
State or quality of being accepted as legitimate, lawful or right. It also refers to validity by virtue of political or public acceptance.
Legislative Day
A day in which a legislative session takes place.
Legislative Oversight
The power or responsibility of the legislature to review operations of executive agencies, ministries or departments.
Majority
Either ‘more than half’ (absolute majority) or ‘the largest number’ (simple majority).
Majority Leader
Spokesman and floor leader for the majority party in each house.
Minority Leader
Spokesman and floor leader for the minority party in each house.
Ombudsman
A public official or body that is appointed by the legislature to investigate complaints by individuals about the activities of government agencies. E.g. this function is performed in the Senate and House of Representatives by their Committees on Public Petitions.
Petition
A letter, often signed by many people, making a specific request to the Legislature.
Preamble
Introductory part of the constitution setting out its history, the values and aspirations of the people, and authority under which the constitution is made. Also described as the enacting clause of the constitution usually starting with the phrase “We the People...”
Presiding Officer
Member of the legislature elected by fellow members to preside over its proceedings, regulate debate and interpret its rules impartially. The President of the Senate, Deputy Senate President, Speaker and Deputy Speaker are presiding officers.
Principal Officers
Other elected members of the leadership of the National Assembly, including its presiding officers.
Promulgate
Put a law into effect by a formal proclamation.
Proportional representation
A system of electing members of the legislature where the number of seats allocated to a particular party is determined by the percentage of votes won by that party.
Quorum
The number of members of a House or Committee required by law or rule to be present before they can conduct official business.
Quota
An assigned share of legislative seats assigned to a specific group of people (e.g. women, youths, persons with disability, ethnic minorities, religious groups etc.) to compensate for past injustices or exclusion.
Reading
Refers to the various stages of the legislative process.
Ratification
Making something valid by formally approving or confirming it: ‘a referendum may ratify a constitution’; ‘National Assembly may ratify a treaty’.
Recess
A temporary halting of legislative business.
Referendum
A popular vote by the electorate to decide a political issue, not to choose representatives.
Repeal
A legislative act to remove a provision from a law or an enactment from a body of laws.
Report
A written or verbal statement by a Committee to the National Assembly giving the results of an inquiry or recommendations on a bill.
Rescission
Resolution
Expression of the will, wish, or direction of the Legislature. A resolution generally does not have the effect of law.
Rules
Rules adopted by each chamber to govern its operation and procedure. May be also called Standing Orders.
Sergeant-at-Arms
The head of security in the legislature. Keeps order during legislative proceedings and attends to the Senate President or Speaker when he/she enters or leaves the Assembly Chamber.
Session
One of the time periods into which a Legislature is divided and convened, usually consisting of a number of separate sittings. The constitution mandates sittings of not less than one hundred and eighty-one days in a year. The National Assembly’s annual sessions typically commence in June.
Schedule
Appendix to a statute or constitution
Sitting
A meeting of the Legislative Assembly within a session.
Standing Committee
Permanent committees established under the standing rules of each chamber and specialising in the consideration of particular subject areas.
Sovereignty
Absolute power of a country to control or govern its territory and population.
Sponsor
A member who authors or agrees to introduce a bill or measure.
Tier of government
Level of government.
Unicameral
Legislature composed of one chamber.
Veto
An official action by the President that nullifies legislative action in the passing of a bill or appropriation.
